Problems with the braking system are considered critical and must be eliminated immediately. The force from pressing the brake pedal is transmitted to the brakes through the master brake cylinder (MBC), which converts line pressure to hydraulic pressure. The brake fluid passing through the master cylinder transfers it further to the brake calipers, or as they are also called, slave brake cylinders. In these, the hydraulic pressure is converted back to linear pressure, pressing the brake pads against the brake rotor, which is rigidly connected to the wheel. This friction prevents the wheels from spinning, slowing it down when the driver applies the brake.
Often the master cylinder is the culprit for brake malfunctions. It is mechanically connected to the brake pedal. Next, MBC is considered in order to find out the cause of the breakdown and be able to repair it on his own. In the process of diagnostics, it is necessary to distinguish and weed out malfunctions of other elements of the brake system, having information about their wear and maintenance.
Do You Know How Master Cylinder Work?
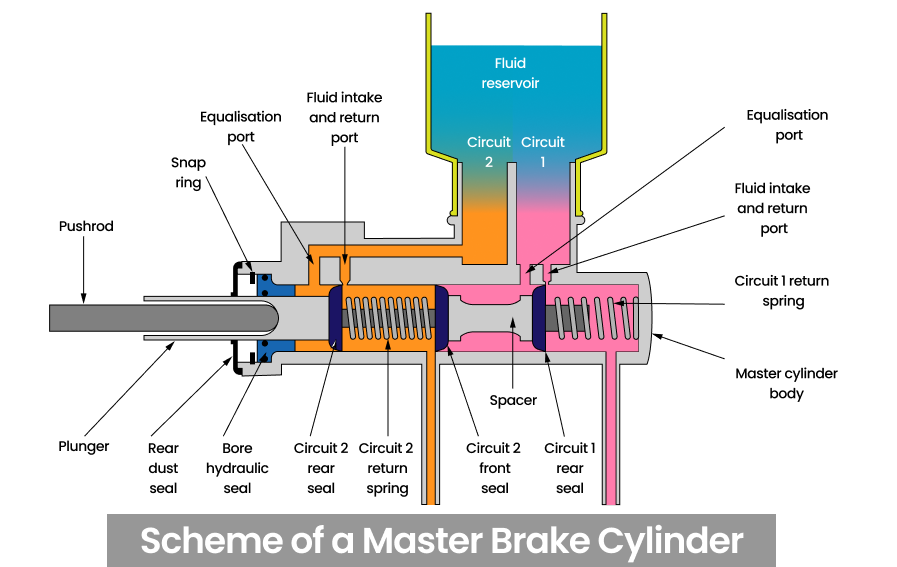
NOTE: MBC acts in conjunction with a vacuum booster (not shown in the picture), which helps to put pressure on the pistons. This allows for quicker system response and ease of action for the driver.
Next, we will look at the problems, but before that it would be nice to understand how the brake master cylinder works. An expansion tank is attached to its body on top, where there is a surplus of fluid. Internally, the element is divided into 2 cylinders with separate pistons. The pushrod from the brake pedal is attached to the first piston. The brake circuit tubes are attached to the lower ports – separately for the front and rear wheels. When the brake pedal is depressed, the rod pushes the brake fluid out of the first cylinder, and since the hydraulic fluid is not compressed, also from the second cylinder. So, usually, the front brakes (main) and immediately the rear (secondary) brakes are applied first. But it happens that these two contours are located diagonally on some cars.
Symptoms of Master Cylinder Failure
The general technical condition of the vehicle (including the braking system) can be checked using a diagnostic scanner. When choosing him, you need to take into account that it can scan the errors of the brake system, including the ABS system. The BMC wears out like all mechanical-hydraulic systems. Mostly rubber seals can start leaking, while the springs and stem usually remain functional for the life of the vehicle.
The hydraulic brake system consists of many parts that can become unusable: brake lines, wheel cylinders, brake calipers and brake pads. For proper diagnostics, as we said above, it is worth understanding how the brake system works, and it is also advisable to check the errors in the ECU that the sensors have collected in it. Next, consider the main symptoms of a malfunction of the brake master cylinder:
Slow braking. It can occur due to the loss of tightness of the seals of the main or secondary brake cylinders, as well as brake lines.
The pedal falls. When the brake is applied, the pedal falls through at the end of the stroke. This indicates that the sealing rings in the cylinders are worn out, and therefore the brake fluid flows over the piston, creating a failure.
Short pedal stroke. The flow of fluid inside the cylinder may be restricted because the fluid intake and/or return port is clogged.
Dirty brake fluid. If the seals in the cylinders and brake lines are not tight or contaminants have entered the brake circuit, the brake fluid loses its properties. It requires replacement along with flushing the brake system, you need to remember this when the time comes for the maintenance of the car.
Caliper sticking. Dirty brake fluid also causes this phenomenon. If the brake line is clogged or the port at the inlet / outlet to the brake cylinder – the brake pad may jam, because the fluid from the cylinder in the brake caliper cannot go back normally to the MBC.
Warning lights. The appearance of the “Check Engine” and “Brake Warning” lights on the dashboard may indicate problems with the pressure in the brake system and / or a low level of hydraulic fluid in it.
Master Cylinder Diagnostics
As you may have noticed earlier, in most cases there is only one source of problems with the brake master cylinder – seal wear. Over time, seals can break and lose their own properties and begin to leak fluid or clog drain ports. If a problem is identified with the seals in the master brake cylinder, it can be solved by completely replacing the device, or replacing only the seals if the cylinder walls do not have mechanical wear. We recommend the first option because motorists are of the opinion that the new rubber seals will not last long, and also because it is a more time-consuming process and may require special skills. We believe that rebuilding the brake cylinder is best left to the professionals and have taken this process outside the scope of this article.
Before checking the MBC, make sure that there are no other malfunctions of the brake system:
- Inspection of wheels. Visually check the wheel assemblies from the inside for brake fluid leaks from the working cylinders.
- Expansion tank. Check the fluid level in the brake fluid expansion tank and its integrity.
- Air leaks. Start the engine. At idle, squeeze the vacuum take-off pipe to the brake booster. If the engine RPM has increased significantly, air is leaking and the master cylinder is most likely working properly.
Drops of brake fluid on the body of the main hydraulic cylinder are a clear sign of a malfunction. Having found a leak, the MBC can definitely be removed and the cause inside it can be looked for. If the leak is caused by the seals, do the following to check it:
Assistant. Unscrew the brake fluid expansion tank cap and have an assistant perform the following operations.
Listen. Listening to the sounds in the reservoir, give the command to the assistant to press the brake pedal.
Gurgling. If the pedal moves easily, and a gurgle is heard in the expansion tank, liquid enters there. The reason is that worn out sealing rings in the cylinders are not able to create pressure in the brake system circuits. Liquid seeps through the seal and into the expansion tank.
We should also check the following. If you feel a seizure or too little pedal stroke. Sit behind the wheel, apply the brake several times. Start the engine by holding the pedal with your foot. If after that it fell to the floor or did not budge, then the master brake cylinder is faulty.
We do an efforts to find, research and recommend the best products. So, we may receive commissions from purchases that you make after following the links in our product reviews.







