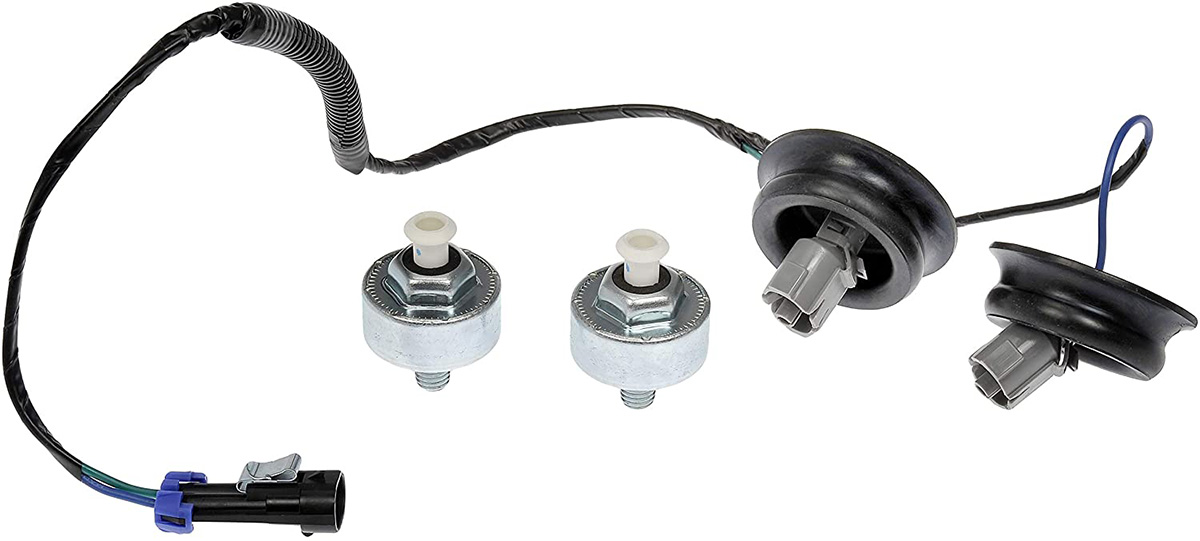

- 1. What is an Engine Detonation?
- 2. How does the Sensor Work?
- 3. 5 Signs of Knock Sensor Malfunction
- 4. 4 Most Frequent OBD2 Error Codes Related With Knock Sensor
- 5. The Reasons of Knock Sensor Malfunction
- 6. Can I Still Drive With a Faulty Sensor?
- 7. Can the Knock Sensor Be Turned Off Completely?
- 8. How to Recognize a Malfunction of the Knock Sensor?
- 9. How Much It Will Take to Replace Knock Sensor?
Failure of the knock sensor causes the engine control unit (ECU) to stop detecting the detonation process during burning of the fuel mixture in the cylinders. Such a problem occurs as a result of too weak or, on the other hand, too strong signal from the knock sensor, which is also named as “detonation” sensor. As a result, the “check engine” light lights up on the dashboard, and the car’s behavior changes due to the engine conditions.
If a car owner knows the signs of knock sensor failure (and, of course, other controllers) and knows how to read the errors shown by the ECU, it can greatly facilitate him to solve problems with the work of the engine and its components.
To understand the question of knock sensor malfunctions, it is necessary to understand the principle of its operation and the functions it performs.
What is an Engine Detonation?
The engine detonation is the process of arbitrary ignition of the gasoline-air mixture without the spark from the spark plugs. It is not a harmless effect. When it affects the pistons, the valves, the cylinder head, the engine as a whole – they are significantly overloaded. In modern cars, sensors are used in control systems to prevent knocking of the engine.
Theoretically, if the pressure in the cylinder exceeds the maximum permissible value for a mixture with gasoline of a certain octane number, autoignition occurs. During the engine knocking, the autoignition process is chaotic, there is no single center of ignition as shown on the picture:
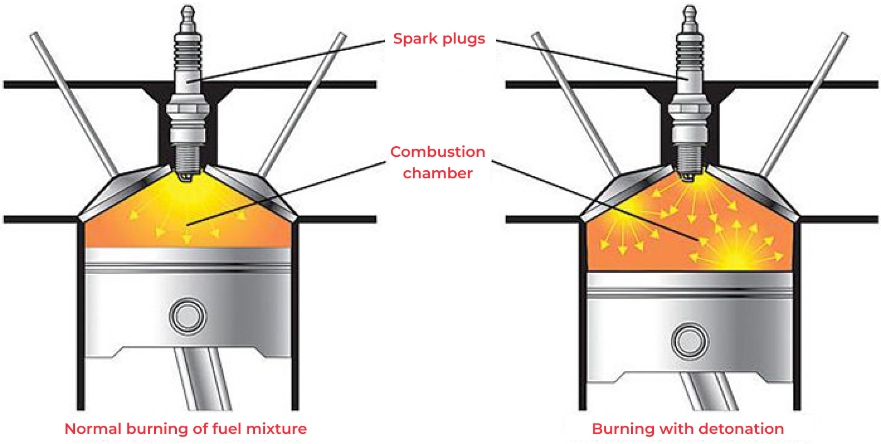
During detonation, the peak pressures in the cylinder are almost twice as high as the maximum pressures during normal combustion. Such stresses can lead to engine failure, even something as severe as a crack in the engine block.
How does the Sensor Work?
One of the two types of knock sensors that can be used in car engines most often – broadband and resonant. But since the first type is already outdated and rare, let’s describe the work of the piezoelectric knock sensors.
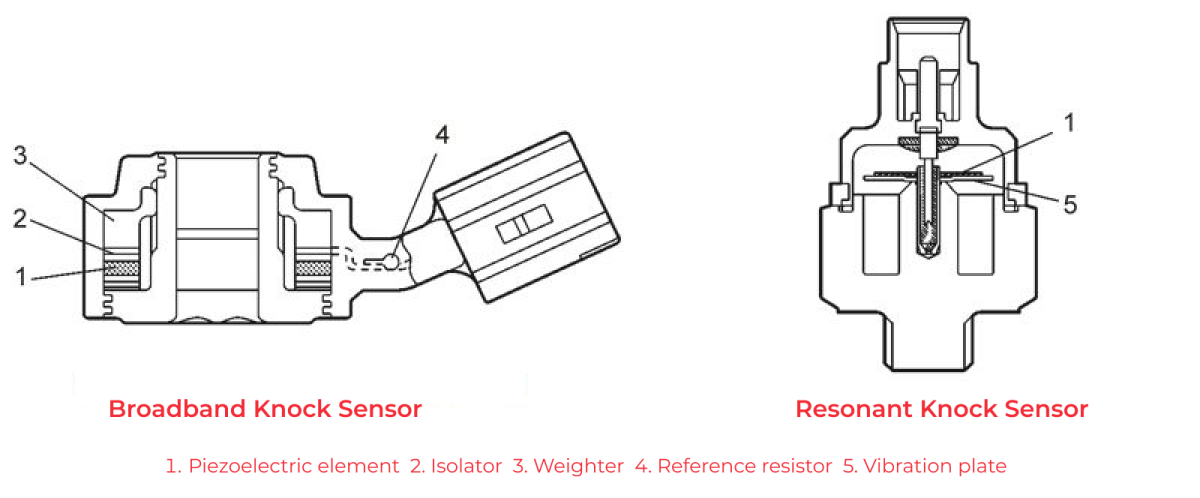
The key element of a broadband type is usually a piezo element, which, when mechanically affected (in this case, by an explosion), supplies a current of a certain voltage to the electronic control unit. The range of perception of sound waves is approximately 6 Hz – 15 kHz. The construction of the sensor also includes a weighting element, which enhances the mechanical effect on it by increasing the force, i.e., increases the sound amplitude of the signal.
The voltage supplied by the sensor to the ECU through the terminals of the connector is processed electronically and then the conclusion is made whether there is detonation in the engine, and, accordingly, whether the ignition advance angle needs to be corrected to help eliminate it. The correction takes place until the detonation is stopped by the joint efforts of the knock sensor and the ECU, after which the sensor again, as it were, falls asleep.
5 Signs of Knock Sensor Malfunction

- “Check Engine” Light. It is detected by detecting errors of the knock sensor. Usually, the reasons for their appearance are the output of the signal from the sensor beyond the permissible limits, breakage of its wiring or its complete failure. The appearance of errors will be indicated by the “Check Engine” light on the dashboard.
- Engine shaking. If the sensor and control system in the engine are working properly, this phenomenon should not occur. The appearance of detonation can be indirectly determined by the metallic sound coming from the running engine (knocking of the fingers). Excessive shaking and jerking while the engine is running is the first way to determine the detonation sensor malfunction.
- Decrease in engine power. This is manifested by poor acceleration or excessive increase in RPM at low speeds. This occurs when an incorrect knock signal causes spontaneous correction of the ignition angle.
- Increased fuel consumption. Since the ignition angle is disturbed, the fuel-air mixture does not meet the optimal parameters. Consequently, the engine consumes more fuel than it needs.
- Difficulty in starting the engine. This is especially characteristic of a cold engine, i.e. at low temperatures after a long idle time (for example in the morning). Although it is quite possible such behavior of the car and at warm ambient air temperature. Read more about possible reasons why the car doesn’t want to start normally.
Of course, all of these symptoms may indicate other malfunctions of the car, and the causes may be completely different sensors. In principle, the detection of problems exactly with the knock sensor is facilitated by the fact that the detonation itself can be determined by ear, but it is still recommended to read the engine errors obviously to be sure of the correctness of the further repair.
4 Most Frequent OBD2 Error Codes Related With Knock Sensor
Signs of knock sensor failure, in general, are very similar to the symptoms of retarded ignition, as in the case of an inaccurate ignition advance angle setting. If the control lamp “Check Engine” lights up on the dashboard in combination with the symptoms of retarded ignition, you need to do the scanner check of the engine.
To diagnose the sensor, you need to read whether there is one of the 4 knock sensor errors and/or errors of the MAF sensor, Oxygen Sensor or Coolant Temperature Sensors, and then view the indicators in real time on the ignition advance angle and composition of the fuel mixture. There are these OBD2 errors, related to the engine knock sensor:
- Error P0325. Often the error P0325 “Break in knock sensor circuit” indicates a problem in the electrical wiring. It may be broken cables or, more often, oxidized contacts. It is necessary to perform preventive maintenance of the connectors on the sensor. Sometimes error P0325 occurs because the timing belt is 1-2 cogs off.
- Errors P0326 and P0327. These 2 errors are usually fixed in the ECU when the signal from the knock sensor is too weak. The causes here are bad contact from the sensor itself, or weak mechanical connection of the sensor to the engine block. To eliminate the error, you can try to apply a rust converter like WD-40 to both the contacts and the sensor itself. It is also important to check the tightening torque of the sensor, as this parameter is critical for its operation.
- Error P0328. It occurs when the signal level from the knock sensor is high and, usually, this error indicates a problem with the electrical wiring, for example, in case of damage of isolation. Another cause of the error P0328 can be the timing belt, which has shifted by 1-2 cogs, therefore it is necessary to check the marks on it.
The Reasons of Knock Sensor Malfunction
Among all the many causes of problems with the engine knock sensor, you can conventionally classify problems with the sensor itself and its wiring, as well as problems not directly related to the sensor. But all of them can equally lead to its bad operation and the engine as a whole, and also lead to very expensive repairs. That’s why we decided not to divide them into two categories. Below we highlighted those symptoms that deserve the most attention, appearing more often than others.
1) Problems with sensor wiring
Usually the knock sensor wiring can be broken, internally short-circuited, or have internal or external isolation damage. If diagnosis shows that there are problems of this nature, they are solved by replacing the wiring or by repairing it.
2) Bad mechanical contact
The sensor may not fit tightly on the engine block, due to which it will not receive vibrations to the full extent. Most often, the detonation sensor is mounted on a threaded joint, which is loose and does not ensure complete adherence of the sensor to the surface of the block. The problem can be solved by simply tightening the threaded connection of the sensor, or by replacing the bolts fixing the sensor. Be sure that spring rings or pad washers are not used for mounting.
3) Total failure of the sensor
The knock sensor itself is a simple enough device, so there is not much to break there, and it fails quite rarely, but it happens. The sensor cannot be repaired, so in case of a complete breakdown it is necessary to replace it with a new one.
4) Carbon buildup
As the car gets older, carbon deposits accumulate on the valves, cylinder walls, and pistons. These carbon deposits can create hot spots that ignite the fuel unevenly.
There are ways to reduce or remove carbon deposits. For example, you can use a fuel and engine cleaner according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
5) Problems with the ECU
Malfunctions in the engine control unit can lead to incorrect perception of information from the knock sensor, and incorrect engine control.
6) Poor fuel quality
The higher the octane rating of the fuel, then the more resistant it is to detonation during compression. If you fill your gas tank with fuel with a lower octane number than your car needs, you are much more susceptible to detonation. If you happen to fill your fuel with a lower octane rating, you can buy an octane booster and pour it into your gas tank according to the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent detonation. Some cars are designed to work with more than one octane number, in which case you do not need to worry, because the engine correction should be automatic.
Can I Still Drive With a Faulty Sensor?
This question is interesting to car owners who encounter this problem for the first time. In general, the detonation phenomenon caused by a faulty sensor is dangerous for engine damage, but in the short term the car can be used. However, at the earliest opportunity it is necessary to carry out appropriate diagnostics and to eliminate the problem.
Also, you should consider that with a faulty knock sensor the engine has an increased fuel consumption and weak dynamics, which will not allow you to use the car comfortably. All this is because the ECU will retard ignition in order to protect the damage of the piston system of the engine when a real detonation occurs.
Can the Knock Sensor Be Turned Off Completely?
There is an opinion that the knock sensor is unnecessary when you fill up with good fuel and under standard car operation conditions. There is no need to do this! A car’s engine is rather difficult and is controlled by a control unit that relies on sensors for its operation. Yes, theoretically your engine will be able to run without failure even without a certain sensor. But a knock sensor is needed first of all for safety and protection from expensive repairs! If you disable the knock sensor, it can lead to the following:
- hole in the engine head gasket with the further expensive repairs
- accelerated wear of cylinder and piston elements, as well as related components
- crack in the engine head with its further expensive replacement
- complete or partial piston burnout
- connecting rod bend
- partial valves burning
How to Recognize a Malfunction of the Knock Sensor?
There are 2 different testing ways that are less and more precise and labor-intensive. So, the first is able to be performed without knock sensor detach, and the other one requires access to the sensor and its contacts.
1) Without sensor detach
It is possible to check the detonation sensor without removing it from the engine block. And at first it is better to do exactly this test, when the sensor is screwed to the block. Shortly the procedure looks like this:
- find the detonation sensor or understand its exact location in the engine block;
- add engine RPM by holding the accelerator pedal and fixing it at the one level, about 1,500-2,000 RPM;
- using a metal object (a small hammer, wrench) make one or two soft (!) strikes on the engine block near the sensor (you even can lightly strike directly to the sensor). After this the engine RPM should become less and you will hear this by ear, otherwise if they are still at the same level – it is necessary to make an additional check.
2) Test with the multimeter
The most accurate way to check if the sensor is working properly is to detach it. You need to disconnect the wiring from it and connect a multimeter in the 2-volt measurement position to its pins. When you tap, the multimeter reading should increase from 0 to several tens of millivolts. If the voltage increases when you strike softly, it means that the sensor is electrically correct.
Related post: The Best Multimeters For Automotive
Also, the good way to check detached knock sensors is with an oscilloscope. Even the shape of the output signal can be determined accurately with an oscilloscope. This check is best carried out at a service station.
It is also essential to carry out a basic check of the integrity of its wiring to check for open, damaged insulation or short circuits. A multimeter is also a must for this purpose.
If the check shows that the knock sensor is in order, but the error is out of sensor signal range, the reason may be in the engine or gearbox, not in the sensor itself. Why? It’s all caused by sounds and vibrations which the detonation sensor may perceive as fuel detonation and incorrectly adjusted ignition angle.
How Much It Will Take to Replace Knock Sensor?

The average cost of replacing a knock sensor ranges from $250 to $400, depending on your car and the specific auto service where the repair will be performed.
Before replacing any components, make sure that you carry out a proper diagnosis. For example, in the case of replacing the knock sensor, you need to make sure it’s the problem, although the symptoms can be very similar to problems with other sensors and engine components.
You could save some money if you do the repair yourself. Then you might consider an aftermarket knock sensor. It won’t cost more than $30 to $100, depending on the car. For example, if you have a Chevrolet Silverado which has 2 sensors, it’s worth replacing them both at once.
Note that the original parts will cost more, and you may need them to keep your warranty on the car.
Standard labor costs for knock sensor replacement by an auto mechanic range from $120 to $300. Costs may vary from car to car, depending on how accessible the sensor is, and access to it requires the removal of many engine components.
Using your knowledge and time, understanding this issue of replacing the sensor on your specific car and working on your own, you may be able to reduce the cost by as much as $200-$350.
We do an efforts to find, research and recommend the best products. So, we may receive commissions from purchases that you make after following the links in our product reviews.










